High Protein Diet Myths - Review for Bodybuilding, Athletics and Weight Loss
Recent research reviews have shown that building and sustaining muscle mass does not require extreme high protein diets and dietary supplements. All the protein that bodybuilders, athletes and active people need, can be provided from a sensible 'normal' diets, supplemented with small extra amounts when building new muscle as part of a body building program.
Many prominent body builders are vegans and don't eat huge steaks. High protein diets, meals and expensive protein supplements may be a waste of money.

Of course all people, especially those undertaking regular training should get a well balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of protein. Researchers suggest that active people should ensure that they consume between 0.8 and 1 gm of protein per kilogram of body weight every day, with extreme athletes and bodybuilders consuming twice these amounts when training or after events or heavy training.

Eating more protein than this is simply wasting money and the shift to a protein-based metabolism may in extreme cases cause risks of kidney disease and other problems.

Generally it is true that protein cannot be stored by the body, and that the muscles are continuously being turned-over and if inadequate amounts are not provided in the diet the body may have to scavenge existing muscle mass to build new muscle. This emphasises that protein it should be a part of every meal, especially evening meals, because the repair and build up of muscles occurs at night during sleep.
Of course after an extreme exercise event such as a marathon or a very intense gym workout when your body has been exposed to an extremely strain and there is some repairing and re-building to be done, extra protein will help, but only for a week or so. Protein intake during these periods could increase to 2-3 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight (double the normal levels). After this rebuilding phase people should quickly return their protein intake to a normal levels.
The Australian Institute of Sport (AIS) is Australia has reviewed the literature of the protein requirements of athletes as part of its Olympic Training Program and other programs for Elite athletes ranging from swimmers, teams sports, athletics, boxers and weight-lifters. Their conclusions are summarised below:
Do athletes, runners and active people need more protein?
Detailed research of the last 20 years has answered this question.
- Endurance athletes in heavy training may require additional protein to provide any extra energy costs due to their training and to help in the recovery and repair process following exercise.
- Strength athletes, and body builders who are trying to build muscle size and strength, require extra protein during the initial stages of very intensive training exercise.
- The amount of extra protein required is only marginally more than that required for other generally active people.
- Athletes, who are young and growing may have extra protein requirements.
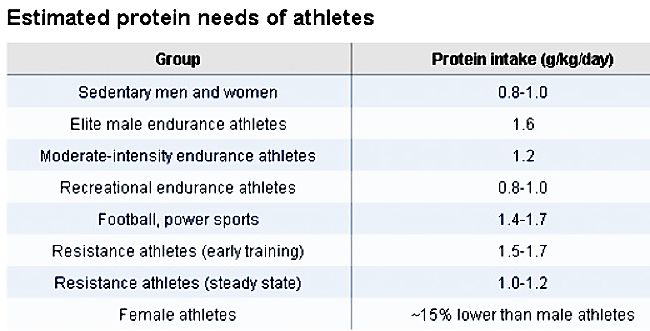
The table below summarises protein requirements for different types of athletes engaged various types of activities compared to more or less sedentary males and females. Women generally require about 15% less protein than males.
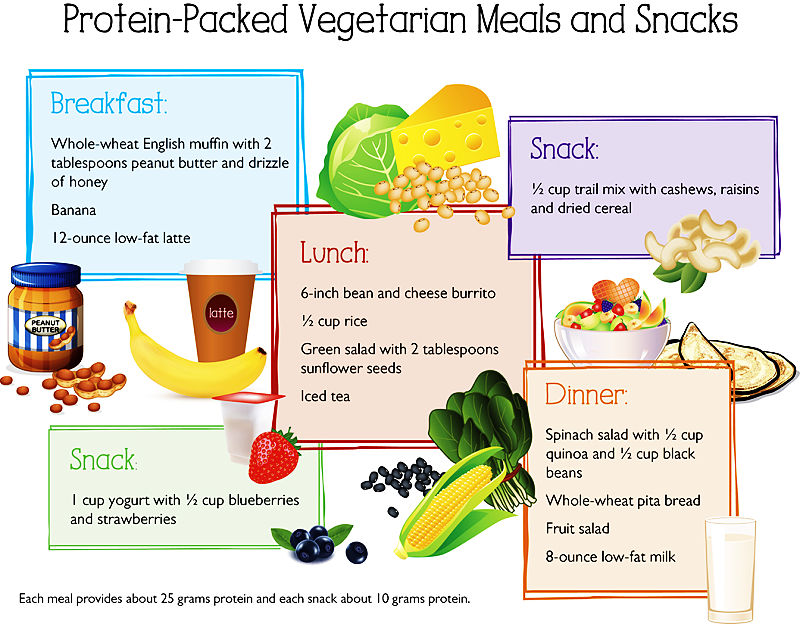
Should Training Athletes Eat Protein-rich Foods and Supplements?
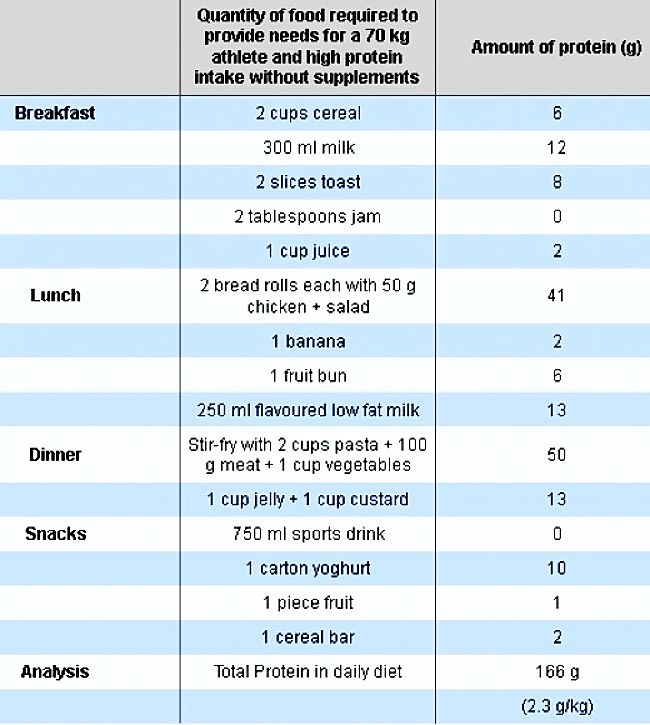
Do athletes, weight trainers and body-builders need to change their diet to meet the extra protein they need? Do they need to concentrate on very high protein foods, or take protein supplements? Several surveys of the diets of body builders and athletes shows that many of these people eat in excess of 2.0 gm/kg body mass per day by eating high-protein diets and supplements. Is this necessary or wise. The table below shows that a 70 kg athlete can easily get in excess of 2.0 gm/kg body mass per day by eating a 'normal' diet.
Protein Needs Can be Provided by 'Normal' Foods and Diets
Athletes Involved in Heavy Programs should Eat Extra Protein Immediately after Exercise
Recovery processes for athletes and body builders are very complex and include rehydrating, refueling and repairing. General body and muscle protein metabolism is in a constant state of flux between breaking down protein and maintaining and rebuilding protein and muscle fibers. During exercise the balance shifts towards the breakdown of protein. During the recovery process following exercise routines or events the balance tips in the opposite direction.
Taking in extra protein immediately following exercise improves muscle rebuilding and the retention of amino acids, the building blocks or proteins in the blood stream, and generally provides for protein balance. This elevated rate of protein metabolism lasts for about 24 hours. It is important for athletes to consume protein right throughout the day, before rest at night and immediately following exercise.
Studies show that the effect of post-exercise protein is enhanced when the protein is combined with carbohydrate. So protein-carbohydrate snack or meal after a workout is a very good idea for both muscle repair and to replenish the carbohydrate fuel store in the muscles in the form of glycogen levels.
As shown below there is no need for high-protein shakes as many snacks or light meals can achieve this. However homemade protein bars and shakes can be quick options.
See: Homemade Protein Bar Recipes and How to Make a Protein Shake
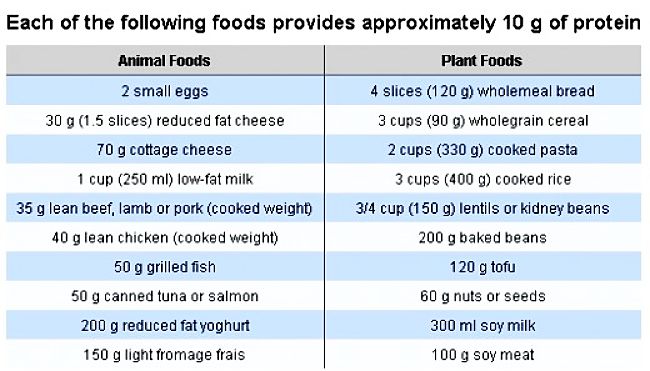
Protein can be Provided Equally Well by Animal and Plant Sources
Conclusion
Athletes, weight lifters and body builders can get all the protein they need from a good balances diet consisting of standard foods.
Sometimes athletes may need a supplement or extra protein. However many commercial protein supplements are very expensive and are highly processed, many with doubtful or unknown ingredients that may include hormones. Many supplements have few vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. So you are probably better off making your own, or simply eating high-protein natural foods that provides both protein and carbohydrate. Good alternatives to commercial protein powders include homemade protein bars, homemade protein shakes and protein-fruit smoothies and liquid meal supplements. One simply way to add extra protein is to add 20 gm of skim milk powder to regular milk or to a smoothie.
Does a High-Protein Help with Weight Loss?
Although high protein diets (and low carb diets) are very popular, they are not recommended for athletes who need a ready source of energy. However if an athlete is trying to lose weight eating more protein may help. Protein can help suppress appetites when it is used as bulk replacement for high calorie carbohydrates in meals. Increasing protein intake in diets may help people reduce their calorie intake and so help control weight. However there is nothing magical about protein and this strategy works because high-protein foods have lower calorie densities and keep people feeling 'fuller' for longer. These outcomes can be achieved in other ways. See: High Protein Low Calorie Foods